What is Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
A person with borderline personality disorder (BPD) experiences extreme volatility in their relationships, emotions, and sense of self. Extreme mood swings, trouble controlling their emotions, and impulsive conduct are common in people with BPD. In addition, they could struggle to establish and preserve healthy relationships and suffer from a problematic sense of self.
Signs and Symptoms of BPD:
Usually, BPD first manifests in adolescence or early adulthood.
Here are a few typical indications and symptoms:
- inability to sustain a consistent sense of self-identity
- interactions that are unstable and passionate, characterized by idealization and depreciation of others
- impulsive actions with the potential to harm oneself
- Suicidal thoughts or threats regularly, or self-harming actions
- strong emotional responses to trying circumstances
- persistent emptiness
- Inability to control one’s wrath
- brief periods of psychosis or disassociation from reality
Diagnosis:
A mental health practitioner will diagnose BPD after doing a comprehensive evaluation that includes talking about symptoms and experiences. For BPD, there is no particular laboratory testing.
Diagnostic Criteria for DSM 5:
The official resource for diagnosing mental health disorders, including BPD, is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR).
A person needs to meet at least five of the following nine requirements to be diagnosed with BPD:
- persistent emptiness
- Emotional instability as a result of daily occurrences
- frantic attempts to prevent imagined or actual abandonment
- Identity disruption is characterized by at least two potentially self-damaging areas of obsessive activity and a noticeably or persistently unstable sense of self
- Anger that is inappropriate, excessive, or difficult to control
- An unpredictable and intensive pattern of relationships that exhibit extremes of idealization and devaluation, commonly referred to as “splitting”
- Recurrent acts of self-harm, threats, or suicidal conduct
- Brief paranoid thoughts brought on either stress or acute dissociative symptoms
Treatment of BPD:
Though historically difficult to treat, there are BPD treatments that work:
The best-researched treatment for borderline personality disorder is dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which emphasizes emotional control, mindfulness, and constructive interpersonal interactions.
Family-oriented therapies have the potential to be advantageous for children and adolescents.
For young people with BPD symptoms, structured day programs with significant behavioral management components may also be beneficial.
Psychotherapy: Due to strong emotions and impulsivity, treatment might be difficult, but it can also be helpful.
Drugs: Drugs can be used to treat certain symptoms, such as sadness or impulsivity. However, treatment should be utilized in addition to medicine, as medication is not a cure for BPD.
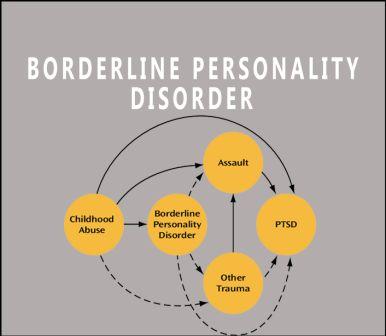
Psychiatric behavior is due to many reasons, such as anxiety, depression, mood swings, mental illness, and a bad self-image. These symptoms are most familiar with Borderline Personality Disorder. It is called spontaneous reaction, and its leading cause is relationship disruption.
Patients with borderline personality disorder (DSM-5) experience depression, intense anger episodes, and anxiety that last for two hours to some days.
The victims of this disorder have to face changed opinions frequently, and this improved mood is the leading cause of unstable relationships. This emotional sensitivity is involved genetically. Therefore, it is the main role of a biological factor that influences such people.
Due to intense emotions, the victim has to suffer for a long time. Heritable traits, or impulse control, are challenging for such patients to control.
Patients who live with borderline personality disorder imagine abandonment and experience cutoff communications.
Unstable relations with loved ones and family turned into devaluation and anger. This is the main reason for the personal, distorted image.
Environmental Factors
Moreover, environmental factors contribute also. In the case of Maria, she has experienced abruptly broken relationships. This state has made her a victim of Borderline Personality Disorder, and she feels that everyone dislikes her.
Historically, this disease has been deemed challenging to treat.
With recent advancements and evidence-based meditation, people with this disease can have fewer symptoms than before.
Specialized treatments help reduce emotional sensitivity. Individuals living with borderline personality disorder have been seen to have an increased inclination to self-harm.
This damaging behavior occurred frequently and often converted into suicidal behavior.
Maria had experienced a massive level of anxiety and depression when she learned that her boyfriend would not marry her. Pressed circumstances made her feel bad and presented a situation of self-damage.
Such behavior causes substance abuse, dangerous behavior, late-night walks, and attempts to commit suicide. The recurring feelings of suicidal thoughts are highly personality-damaging and intense.
Prognosis with Borderline Personality Disorder DSM 5
The prognosis for the individual living with borderline personality disorder is different. These days, the most famous treatment is psychotherapy. In the group setting, one-on-one activities are conducted that help patients develop social skills.
It is the way they get to know how to build trust and express it. In this way, the therapist forms a bond with the patient.
Medication is another way to get rid of symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder. The medication option is usually suitable to reduce the suicidal behavior of the patient. Every patient needs intensive care, and it also depends on the severity of symptoms.
The method of outpatient treatment takes time, and studies suggest that individuals go through this kind of treatment do not exhibit Borderline Personality Disorder DSM 5 characteristics.
The clinical expressions of depression and anxiety are common in these individuals.
Borderline Personality Disorder DSM 5 is seen increasingly in adolescents as a developmental disorder. Research findings suggest that treatment can reduce the duration of illness as well as chronicity.
According to research findings, it is evident that this disease is associated with low socioeconomic status; despite the same level of intelligence, individuals experience its symptoms.
Individuals with this disorder tend to experience multiple personalities and are unable to have long-lasting happiness. They always try to be perfect, so become victims of depression.
In a cynical mood, such patients try to disengage attention, so they experience attentional maintenance.
Crucial points to remember:
BPD frequently coexists with other mental health issues such as substance misuse, anxiety, or depression. BPD sufferers may encounter considerable distress and difficulty going about their everyday lives. People with BPD can learn to control their symptoms and have happy, meaningful lives with the right care and assistance.
Acquaint yourself with BPD:
Gaining knowledge about the illness can empower you and help you make sense of your experiences. But make sure you only trust reliable sources. Some good ones are as follows:
Borderline personality disorder is covered by the National Institute of Mental Health at https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics.
A borderline personality disorder is defined by the American Psychiatric Association at https://dictionary.apa.org/
Think about support networks:
Making connections with people who are cognizant of your situation can be immensely beneficial. Support groups, whether virtual or physical, offer a secure environment for people to exchange stories and get motivation.
For advice on local support groups, speak with NAMI or mental health specialists in your community.
Create constructive coping strategies:
You can take steps to manage your symptoms while you wait for medical assistance. The following materials can assist you in cultivating constructive coping mechanisms:
Resources are available at https://dialecticalbehaviortherapy.com/ and https://www.samhsa.gov/mental-health.
Obtaining Assistance:
You should get professional assistance for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan if you think you or someone you know could have borderline personality disorder (BPD).
The following resources may be of assistance:
National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): 1-800-950-NAMI (6264) or https://www.nami.org/Home
National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 988
See https://www.samhsa.gov/mental-health for MentalHealth.gov.