Plato, an ancient Greek philosopher, presented many philosophical theories based on Western thought. Socrates was his teacher, and he was Aristotle’s Teacher. His famous writings showed the touch of beauty, justice, philosophy, equality, and theology with the aesthetics.
Under the epistemology and language philosophy, the Academy of Plato and Aristotle was built in Athens. This is the Western world institution that serves the higher learning approach. By the period he was born, there needed to be more primary sources, and in his life, many scholars were influenced by contemporary theories and classical historians.
Plato and Aristotle in Western philosophy
Plato and Aristotle are two of the most influential philosophers in the history of Western philosophy. They lived in ancient Greece during the 4th century BCE. They made significant contributions to various fields of knowledge, including metaphysics, ethics, politics, and epistemology.
Here’s an overview of their ideas and their contributions to philosophy:
Plato:
Plato was a student of Socrates and the teacher of Aristotle. He is best known for his philosophical dialogues, written as conversations between Socrates and other characters. Plato’s philosophy explored a wide range of topics and introduced several key concepts and theories:
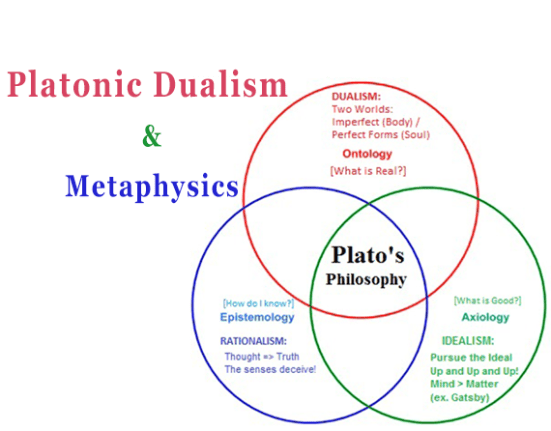
- Theory of Forms: One of Plato’s central ideas is the theory of Forms or Ideas. According to this theory, the physical world we perceive is an imperfect reflection of an ideal realm of Forms. These Forms are eternal, unchanging, and perfect essences representing the true nature of things.
- Dualism: Plato proposed a dualistic view of reality, distinguishing between the physical realm (the world of appearances) and the metaphysical realm (the world of Forms). He believed that the soul was immortal and existed before entering the physical body.
- Allegory of the Cave: In Plato’s famous allegory of the Cave, he illustrates the journey from ignorance to knowledge. He describes prisoners chained inside a dark cave, perceiving only shadows on the wall. Through philosophical enlightenment, the prisoners can escape the cave and better understand reality.
- Ideal State: Plato also presented his vision of a perfect state in his work “The Republic.” He argued for a just society ruled by philosopher-kings with a hierarchical structure and specialization of roles.
Aristotle:
Aristotle was a Plato student and later became Alexander the Great’s tutor. His philosophical ideas differed from Plato’s, and he made significant contributions to logic, metaphysics, ethics, and natural sciences.
Some of his key concepts include:
- Teleology: Aristotle’s philosophy incorporated the notion of teleology, the study of purpose or final causes. He believed that everything in the natural world has a purpose or end goal toward which it strives.
- Four Causes: Aristotle introduced the concept of the Four Causes as explanations for the existence and behavior of things. These causes are the material cause (what something is made of), the formal cause (its form or essence), the efficient cause (the agent or force that brings it into being), and the final cause (its purpose or telos).
- Virtue Ethics: Aristotle’s ethical theory focuses on the development of virtues or excellent qualities of character. He emphasized the importance of moderation, balance, and cultivating virtues to lead a good and fulfilling life.
- Logic and Reasoning: Aristotle made significant contributions to the field of logic. He developed the syllogistic logic system, which examines deductive reasoning and the relationship between premises and conclusions.
The Influence of Plato and Aristotle on Philosophy:
Plato and Aristotle’s works have had a profound and enduring impact on Western philosophy. Plato and Aristotle’s ideas continue to shape philosophical discourse and have influenced numerous subsequent thinkers throughout history. Their contributions have extended to areas such as ethics, metaphysics, political philosophy, epistemology, and the philosophy of mind.
Plato’s influence can be seen in the development of idealism and the concept of transcendent truths. While Aristotle’s ideas have been foundational to fields such as logic, biology, and ethics. Their philosophies provide a rich tapestry of concepts and theories that continue to be studied. These ideas are debated, and expanded upon by philosophers and scholars today.
Plato’s Biography
Artisan was the father of Plato and belonged to the Greek aristocracy. His mother was Perictione and historically related to the 6th century Solon, i.e., a Greek statesman. According to some scholars, the name Plato was given by his grandfather, and the evidence shows that he was the eldest son in the family. By then, the curriculum he studied depicts Pythagoras and Cratylus with the Parmenides.
These studies laid the foundations of metaphysics and epistemology by Plato. This shows the concept of God. The actions of God and the independent activities of human beings seem to be exclusive alternatives.
For instance, if God’s foreknowledge is considered absolute and every occurrence in the universe is attributed to God. So, it becomes challenging to explain that human choices are independent. The same is true if God’s grace is a noble choice that may benefit the human being. In this way, the role of God as omniscient or omnipotent becomes less prominent. However, the vexed philosophical puzzle is suitable to handle the issue of free choice.
Aristotle-The Scholar
He was the Greek scholar, born in 384 BCE. He was an intellectual figure in Western history and secured this position nicely. The scientific and philosophical system he presented showed a developed framework of scholasticism and Islamic philosophy about medieval. In the Reformation, renaissance, and Enlightenment, the concepts of Aristotle’s thinking merged into these schools of thought.
Aristotle Intellect
His intellectual range was vast, of the world philosophies covering most of the arts and other arts subjects like botany, ethics, biology, mind philosophy, metaphysics, and poetics.
He presented formal logic and theoretical as well as observational theories. As the most outstanding philosopher, his contribution to the sciences and ethics is excellent. He provided what makes a human life suitable and what worthy objects, attributes, and values are.
Aristotle’ Biography
Aristotle’s life and thoughts have contributed to the development of many theories. He presented the logical refutation of different arguments and the role of the systematic treatise based on formal logic. Scholarly thoughts have shown the values of life and the contribution of positive values. Firstly, the belief that all humans have to face God one day is purely due to the spiritual approach of an individual.
Considering Plato and Aristotle’s transitions, one will agree to the concepts of the afterlife and the day of judgment only if they also believe in the exclusive power of God to control the whole universe.
On the other hand, the negative side of this approach is that it made human freedom quite conserved and confined to specific criteria as prescribed by the particular religion. For instance, God orders its people to behave ethically according to His standards to become successful on the Day of Judgment.